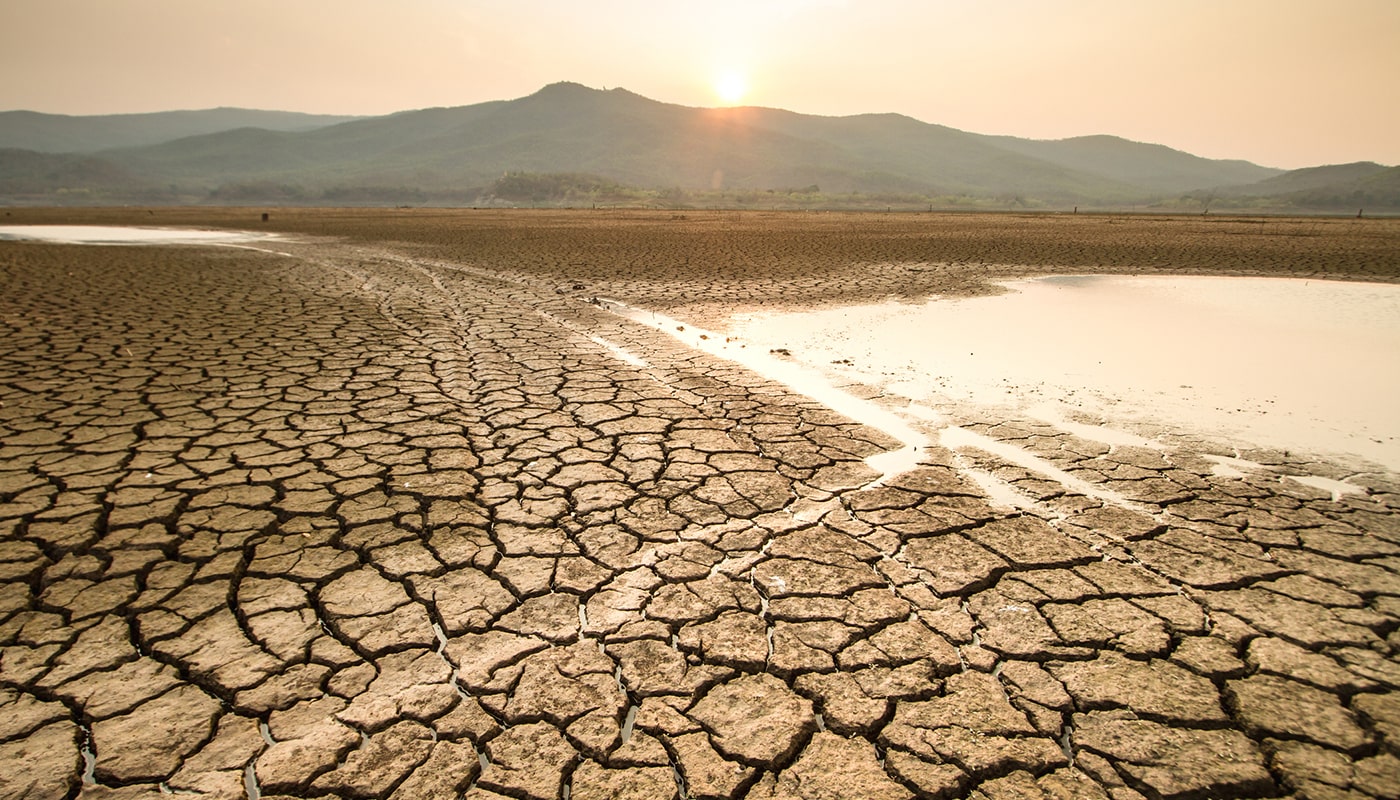
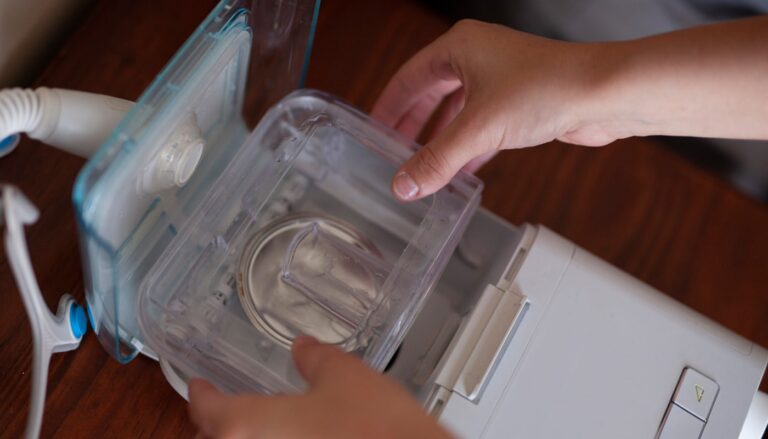
Imagine you’re in a small town where the tap runs dry. The nearby hospital scrambles as their sterilization processes are hindered, and homes struggle to find clean water for basic hygiene and medical needs. This is not a dystopian novel but a reality for many during a sterile water shortage. Such crises not only thirst the body but also strain the mind. Water is fundamental to life for hydration and crucial to countless medical and daily routines. Yet, worldwide, communities face an escalating crisis: sterile water shortages. This issue is not merely about scarcity but touches on the complexities of ensuring water purity critical for health-related needs, from hospital settings to home-based health care like CPAP therapy. The ramifications of this shortage stretch beyond the physical, delving deep into the psychological well-being of those affected. As sterile water becomes harder to secure, the stress and anxiety among those dependent on it for medical and personal hygiene purposes increase significantly. This article will explore the psychological toll of water shortages on individuals and communities.
It also explores the role of reliable water sources, like Aquapap’s vapor-distilled water, in alleviating some of these stresses. By understanding the depth of this issue, we gain insight into the physical and mental resilience required to combat the effects of water scarcity. This discussion sets the stage for a deeper exploration into how consistent access to purified products can be a significant step towards safeguarding both physical and mental health in times of crisis.
Secure your health with Aquapap’s vapor distilled water—shop now for peace of mind!
Understanding Water Shortages
Water shortages are an increasingly critical issue across the United States, impacting not just the arid regions traditionally associated with drought but also areas less accustomed to water scarcity. The causes are multifaceted, involving shifts in climate patterns, increased water demand due to population growth, and aging infrastructure unable to manage and distribute water resources efficiently.
From 2001 through 2017, there were 37 reported shortages of sterile solutions in the U.S., with saline shortages being the most common. The average duration of resolved shortages was approximately 14 months. The peak of these shortages occurred in 2017, with 12 new shortages reported, largely due to the impact of Hurricane Maria on manufacturing facilities in Puerto Rico. This contributed to severe disruptions, notably the longest-running unresolved shortage of 5% dextrose/0.45% sodium chloride starting from October 2007.

In the western United States, states like California, Arizona, and Nevada have long faced significant water shortages due to prolonged droughts exacerbated by climate change. These conditions strain the available water sources crucial for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation. The statistics are stark; for instance, reservoir levels in California have periodically dropped to less than 30% of their capacity during peak drought periods, triggering state-wide water conservation measures.
The situation is no less severe in the Southeast, where states like Georgia and Florida experience water shortages due to overconsumption and sporadic rainfall patterns. Here, the competition for water resources is not just among local communities but also involves disputes over water rights with neighboring states.
Urban areas across the country are also feeling the effects of water shortages. Cities like Atlanta and Los Angeles have implemented water restriction ordinances during particularly dry months to conserve water. These measures, while necessary, underscore the broader impacts of water shortages on daily life and the economy.
These water shortages are profound, affecting everything from the cost of food production to the operational capacity of hospitals and healthcare facilities that rely on sterile water. The ripple effects can be seen in increased food prices, compromised healthcare services, and heightened public anxiety about resource stability.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from public officials, private sectors, and individuals. Innovations in water conservation and management, such as recycling wastewater and improving irrigation efficiency, are part of the solution, as are policies aimed at reducing overall consumption and protecting water sources from pollution.
By understanding the scale and impact of water shortages, communities, and policymakers can better prepare and respond to this growing challenge, ensuring that the population’s physical and psychological health is safeguarded.
Psychological Impacts of Water Scarcity
The psychological impacts of water scarcity extend far beyond the immediate stress of securing daily needs. Long-term water insecurity can lead to chronic stress, anxiety, and depression, deeply affecting communities and individuals. This section explores these mental health effects, supported by academic research and real-world examples, to illustrate the depth and breadth of this issue.
Chronic Stress and Anxiety
Water scarcity creates an environment of perpetual uncertainty, where individuals and families constantly worry about meeting basic needs. This constant stress can escalate into anxiety, especially in households responsible for young children, the elderly, or the chronically ill who need consistent water for health-related purposes. Studies indicate that prolonged exposure to such stressors can disrupt sleep patterns, impair cognitive function, and even lead to long-term psychological disorders. Water scarcity instills a constant fear of running out, deeply affecting daily mental peace. For example, families may experience heightened anxiety when rationing water for essential needs, affecting their overall mental health. Longitudinal studies from drought-prone areas like the Central Valley in California highlight an uptick in anxiety and stress disorders among residents as water levels decrease.
Depression and Helplessness
As water sources become increasingly unreliable, feelings of helplessness can emerge. Research from communities experiencing severe droughts shows a correlation between water scarcity and increased rates of depression. The inability to control or improve one’s situation may lead to persistent despair, particularly acute in regions where economic activities are closely tied to water availability, such as farming. Prolonged droughts or consistent shortages can lead to a profound sense of helplessness, contributing to depressive symptoms. Psychologists note that such environmental stress can lead to a feeling of loss of control, which is a significant predictor of depressive disorders. This can be particularly devastating in agricultural communities as water availability directly impacts livelihoods.
Social Tension and Conflict
Water scarcity can also heighten social tensions, leading to community conflicts. When resources are scarce, competition intensifies, potentially leading to interpersonal and inter-community strife. This social instability contributes further to the psychological burden faced by individuals, compounding stress and anxiety levels. Scarce resources lead to increased competition, which can exacerbate community tensions and lead to conflict. Psychological research suggests that resource scarcity can strain social relations and increase aggression, further impacting community mental health.
Impact on Children and Youth
Children are particularly vulnerable to the psychological effects of water scarcity. Uncertainty and stress in the family environment can affect their emotional and psychological development. Schools in water-scarce regions may also face operational challenges, impacting educational opportunities and social development, further influencing their future mental health. The instability caused by water scarcity impacts children’s psychological development. Schools may struggle to maintain sanitation, reducing attendance and lowering educational outcomes, which affects children’s long-term mental health prospects.
Coping Mechanisms and Resilience Building
Despite these challenges, human resilience often manifests through adaptive coping strategies. Community support programs, local initiatives to secure water supplies, and mental health services can play crucial roles in mitigating the psychological impact. Initiatives focusing on sustainable water use and community-based water sourcing can empower communities, reduce anxiety, and restore a sense of control. Despite these challenges, communities often develop unique coping mechanisms. For instance, some communities implement shared water access points to ensure equitable distribution, which can also serve as community bonding and support centers, helping to alleviate individual stress.
Recommendations for Policy and Intervention
To reduce these psychological burdens, it is critical for policies to not only focus on improving physical water infrastructure but also on integrating mental health support in community planning and disaster response strategies. This could involve training community health workers in recognizing and treating drought-related psychological issues and providing resources for mental health care during times of water scarcity.
By understanding and addressing these issues, we can better support affected populations, building more resilient communities in the face of growing environmental challenges.
Don’t let water shortages impact your life—choose Aquapap for reliable water solutions.
The Particular Strain on Health-Dependent Individuals
Sterile water is a critical resource in healthcare, required for a myriad of medical procedures including but not limited to the preparation of medications, cleaning of medical instruments, and various patient care activities. Its role is vital in ensuring that healthcare services are delivered safely and effectively.
Impact on Healthcare Operations
To find a solution it is important to understand how the sterile water shortage is changing healthcare. The absence of sterile water can severely disrupt routine and emergency medical procedures. Healthcare facilities rely on a steady supply to maintain hygiene, prepare patient treatments, and ensure equipment operation, like dialysis machines. When sterile water shortage occurs, the risk of infections increases, surgical procedures may be delayed, and the overall quality of care is compromised. This can lead to operational inefficiencies and a spike in healthcare costs due to the need for alternative solutions or treatments.
Vulnerability of Specific Populations
Particularly impacted are the elderly, infants, and immunocompromised individuals who require sterile water for everyday medical use. These populations are at a higher risk of developing complications such as infections if sterile water is not available for routine care like wound cleaning or intravenous nutrition.
Psychological Effects of Water Shortages
The uncertainty and anxiety associated with sterile water shortage can have profound mental health impacts on both patients and healthcare providers. Chronic stress from managing health conditions without adequate resources can lead to psychological distress, which may exacerbate existing health conditions or lead to new health issues.
Community and Healthcare Provider Coping Mechanisms
In the face of these shortages, healthcare providers and communities may adopt innovative coping strategies such as local water purification initiatives or adjustments in medical protocols to extend existing water supplies. These measures are crucial in maintaining some level of care when resources are strained.
Role of Technological Innovations
Our company, Aquapap, contributes significantly with products designed to alleviate these issues. Our vapor-distilled water ensures a dependable supply for medical facilities, reducing the burden on healthcare providers and improving patient outcomes. By integrating advanced purification technologies, we provide a solution that meets the stringent requirements of medical-grade water, ensuring safety and reliability.
Policy and Advocacy for Improved Water Management
We actively advocate for robust water management policies that ensure the continuous availability of sterile water, especially in areas prone to shortages. This involves working with policymakers to improve water infrastructure and supporting initiatives prioritizing distributing sterile water to healthcare facilities first.
Educational Initiatives and Public Awareness
Aquapap is committed to raising awareness about the importance of water management in healthcare settings through educational programs and partnerships with healthcare organizations. By informing both the public and professionals about the potential risks and necessary precautions during shortages, we aim to foster a more prepared and resilient healthcare system.
The challenges posed by sterile water shortage are significant but not insurmountable. Through innovative solutions provided by companies like Aquapap, effective policy, and community engagement, we can mitigate these impacts and support the health and well-being of the most vulnerable populations. Ensuring the availability of sterile water is not just a logistical challenge—it is a critical component of public health that requires collective effort and strategic planning.
Role of Reliable Water Sources in Alleviating Mental Stress
Providing reliable water sources is not merely a practical necessity but a significant psychological reassurance, especially during periods of crisis or scarcity. Aquapap, by ensuring a consistent and dependable supply of vapor-distilled water, plays a crucial role in alleviating the psychological burdens associated with sterile water shortage. This section will explore how stable water resources can help ease mental stress and enhance overall well-being.
Understanding the Psychological Impact of Water Security
Water security significantly influences mental health, with uncertain access heightening anxiety, stress, and psychological distress. Reliable access to clean water, particularly in medical settings or daily health care, directly affects a person’s sense of safety and well-being. The assurance that one can meet basic needs without constant worry reduces mental load and allows individuals to focus more on recovery and less on survival.
Aquapap’s Contribution to Mental Comfort
Aquapap’s products provide a solution that offers peace of mind to users, especially those who rely on sterile water for health-related purposes. By using Aquapap’s vapor distilled water, customers can trust in the safety and reliability of their water supply, which is especially critical for those using medical devices such as CPAP machines, where water quality directly impacts health outcomes. The maintenance of your CPAP is very crucial, therefore you must have the tips for cpap maintenance on hand.
With reliable water sources like Aquapap, mental health facilities can better manage the care environment, ensuring that hygiene and patient care are maintained without the added stress of water scarcity. This stability is crucial in environments where psychological well-being is already compromised.
Expert Opinion on Psychological Benefits
Psychologists specializing in environmental stress highlight the benefits of reliable utilities, noting that consistent access to essential services like water can greatly diminish stress and improve quality of life. They recommend integrating reliable water sources as part of a broader strategy to manage community mental health, particularly in areas prone to shortages.
Supporting Community Resilience
Aquapap’s commitment to providing reliable water sources extends to community support, which can bolster resilience against potential crises. Aquapap helps mitigate the cascading effects of water scarcity on community health and psychological stability by ensuring communities have access to clean water.
Reliable water sources like Aquapap are fundamental to meeting physical health needs and fostering mental well-being. In addressing the psychological aspects of water security, Aquapap demonstrates its commitment to comprehensively supporting its customers’ health, ensuring that their water needs are met with reliability and safety.
Strategies for Coping with Water-Related Anxiety
Water-related anxiety can significantly affect communities facing shortages. This section outlines practical coping strategies and highlights successful initiatives that help manage this anxiety effectively.
Education and Awareness Programs
Educational initiatives are crucial in managing water-related anxiety. Programs focusing on sustainable water use, conservation techniques, and personal responsibility can empower individuals, reducing feelings of helplessness and anxiety. For example, rainwater harvesting and greywater systems workshops can provide valuable skills to manage water resources more effectively.
Community-Based Support Systems
Strong community networks can alleviate the psychological burden during water shortages by ensuring equitable distribution and fostering a sense of solidarity. Initiatives like community water-sharing arrangements or the establishment of local water committees can help manage resources collectively and provide mutual support, which is essential during times of scarcity.
Governmental Intervention and Infrastructure Improvements
Governmental policies play a significant role in water management, especially during shortages. Investment in infrastructure to enhance water storage and distribution capabilities and regulations prioritizing water conservation are critical. Programs that provide subsidies for water-saving appliances or tax incentives for businesses implementing water-efficient processes can also be effective.
Psychological Support Services
Integrating mental health services with community health programs can help address the stress associated with water scarcity. Offering counseling, establishing support groups, and providing stress management resources are essential strategies. These services should be accessible and promoted during water shortages to help individuals cope with the associated anxiety.
Technological Solutions and Innovations
Leveraging technology to improve water management can significantly reduce anxiety related to water scarcity. Innovations like smart water meters, which provide real-time feedback on water usage, can help households manage their consumption more efficiently. Mobile apps that alert users about water levels and suggest daily usage limits can also play a crucial role.
Effective Communication and Media Strategies
Accurate and timely information can decrease uncertainty and anxiety during water shortages. Authorities should ensure clear communication strategies, using media outlets to disseminate practical tips for water conservation and updates about water status. These messages should be consistent and designed to prevent panic, emphasizing community resilience and cooperative efforts.
Preparedness and Resilience Building
Enhancing community resilience through preparedness is vital. This includes establishing emergency water supplies, training residents in water purification methods, and conducting community drills for water rationing. Preparedness plans should be well-publicized and include participation from all community segments to ensure widespread readiness.
Aquapap’s Contribution
As part of our commitment to supporting communities, Aquapap provides reliable, high-quality vapor distilled water that ensures users access sterile water for health-related needs. Our products offer peace of mind and contribute to reducing anxiety during times of water uncertainty.
By employing these strategies, communities, and individuals can better cope with the psychological impacts of water scarcity. From educational programs to technological innovations and strong community networks, these approaches collectively support mental well-being and foster a proactive attitude toward water management challenges.
Experience the purity of Aquapap water. Shop today and take control of your sterile water supply.
Future Outlook and Preventive Measures
As we look towards the future, the necessity for innovative solutions to combat water scarcity becomes increasingly critical. This section will discuss future solutions and highlight the role of innovation in preventative measures, drawing on expert insights to explore how these can be implemented effectively.
Advancements in Water Purification and Recycling Technologies
Innovations in water purification, such as advanced desalination techniques and water recycling systems, are crucial for increasing the availability of potable water. These technologies make it possible to turn previously unusable water sources into viable options and improve the efficiency and affordability of these processes.
Smart Water Management Systems
Integrating smart technology in water management transforms how cities and countries conserve and monitor water usage. IoT-based systems can detect leaks, predict water usage patterns, and optimize water distribution, significantly reducing waste and ensuring water scarcity is managed more proactively.
Enhanced Agricultural Practices
Developing drought-resistant crop varieties and improving irrigation efficiency are vital steps in reducing the agricultural sector’s dependence on vast water supplies. Techniques like drip irrigation and soil moisture sensors can maximize water usage efficiency, decreasing the agricultural impact on water resources.
Policy and Governance
Strong governance and comprehensive water management policies are essential for sustainable water use. Policies must enforce water conservation measures, regulate industrial water use, and support the development and adoption of water-saving technologies.
Public Education and Community Engagement
Educating the public about water conservation and sustainable practices is pivotal in addressing water scarcity. Community engagement programs that involve citizens in water conservation initiatives can lead to more sustainable practices at the local level.
Building Resilience to Climate Change
As climate change exacerbates water scarcity issues, building resilience against its impacts is crucial. This includes investing in infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather conditions and implementing strategies to manage water resources more effectively in the face of environmental changes.
Global Cooperation and Partnerships
Water scarcity is a global issue that requires international cooperation and partnerships. Sharing knowledge, resources, and technologies across borders can help develop solutions that benefit larger populations and lead to more significant innovations in water management.
The future of water management is inherently linked to innovation and proactive strategies. By adopting advanced technologies, enhancing policies, and fostering community involvement, we can significantly mitigate the impacts of water scarcity. As part of this effort, Aquapap continues to provide reliable water solutions, ensuring that our products meet the highest sustainability and efficiency standards, contributing to a more secure water future for all.
Securing Our Water, Securing Our Future
As explored throughout this article, the impact of water shortages extends far beyond the immediate challenge of meeting daily water needs—it affects community health, economic stability, and mental well-being. Aquapap’s commitment to providing reliable, high-quality vapor distilled water is more than just a business model; it’s a vital part of the solution to a growing global crisis. By understanding the deep interconnections between water security and public health and through the innovative strategies discussed, we can address the pressing challenges of water scarcity.
The future requires us to continue pushing for advancements in water technology, supportive policies, and community education to ensure everyone has access to safe, clean water. It’s essential that all stakeholders—from governments to businesses to individual citizens—work together to implement the solutions we’ve outlined. Let us commit to water sustainability as a necessity and a responsibility we all share for the health of our planet and future generations. Shop with Aquapap today and take a proactive step towards safeguarding your water supply and supporting overall well-being.